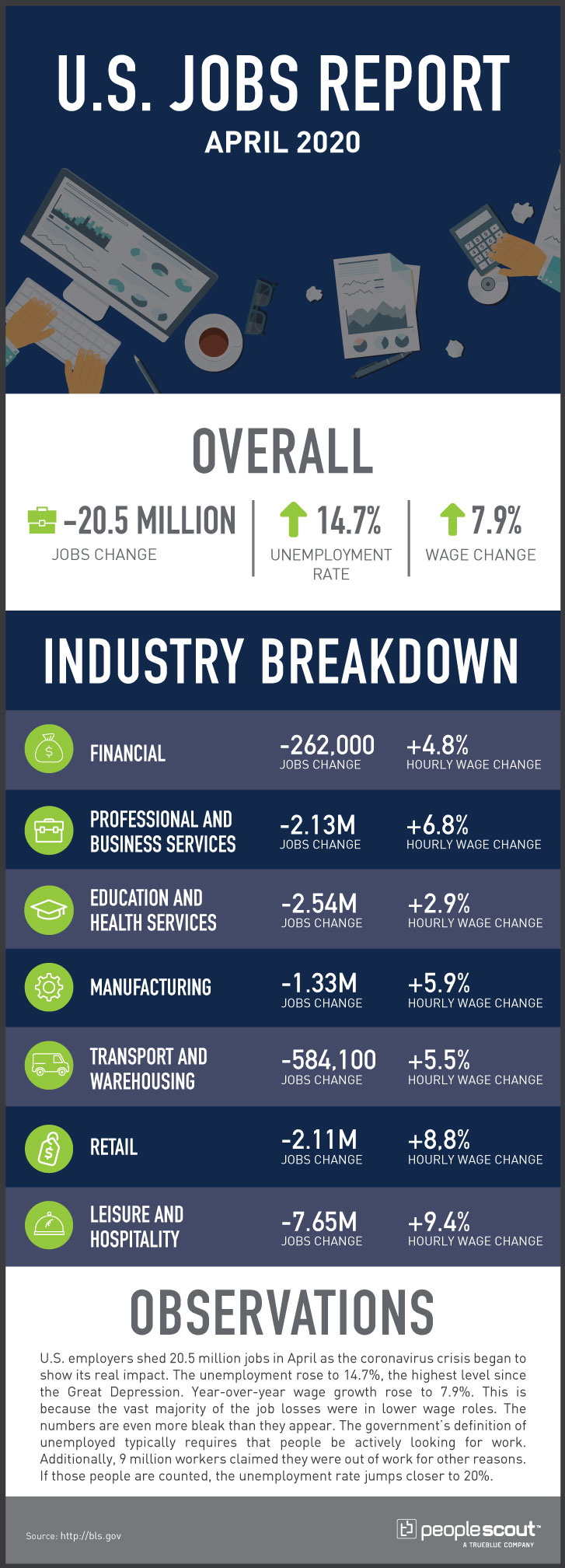
U.S. employers shed 20.5 million jobs in April as the coronavirus crisis began to show its real impact. The unemployment rate rose to 14.7%, the highest level since the Great Depression. Year-over-year wage growth rose to 7.9%. This is because the vast majority of the job losses were in lower-wage roles. The numbers are even more bleak than they appear. The government’s definition of unemployed typically requires that people be actively looking for work. Additionally, 9 million workers claimed they were out of work for other reasons. If those people are counted, the unemployment rate jumps closer to 20%.
The Numbers
20.5 Million: The U.S. economy shed 20.5 million jobs in April
14.7%: The unemployment rate rose to 14.7%.
7.9%: Wages rose 7.9% over the last year.
What We Know
The New York Times reports that the job losses in April alone are more than double the entire previous recession, where 8.7 million jobs were lost and unemployment peaked at 10% in October 2009. The only comparable period was during the Great Depression. In 1933, unemployment reached around 25%, but the government did not report official monthly statistics until 1948.
The leisure and hospitality industry was hit especially hard, with more than 7.65 million jobs lost. That includes all jobs gained in the industry since 1988. Women and minorities were particularly hard hit, with the unemployment rate for Latino and Hispanic workers jumping to 18.9%, and the rate for women jumping to 16.2%.
The massive increase in hourly wages reflects the fact that the majority of the layoffs were in lower-wage positions, while higher-paid, white-collar workers were more likely to hold on to jobs.
What We Expect
The unemployment rate will likely continue to rise in May, according to CNBC, which predicts a rate around 20% for the month.
The numbers may also already be higher than the report currently reflects. MarketWatch reports that some furloughed workers or others who considered themselves employed, even though they weren’t working, were not counted. If those workers were counted, the rate would be around 20% already.
Are There Any Bright Spots?
“Bright spot” is relative in this report. However, 78.3% of those who were laid off in April consider the separation temporary, while 11.1% say the layoff was permanent. This means those jobs could return if the COVID-19 crisis improves, but it also means those layoffs could become permanent if the situation worsens.
There may also be a bright spot for companies who have the resources to hire during the crisis. Harvard Business Review reports that this is an unprecedented opportunity to hire high-quality talent. There are a lot of highly skilled workers, from recent graduates to experienced leaders who are looking for work right now. Employers who can hire during this crisis can bring in strong people who otherwise might not have been seeking new opportunities.




