How could one of the UK’s best known and most trusted brands have no employer brand presence? It might seem hard to believe, but that was the situation the AA faced when they approached PeopleScout’s Talent Advisory practice to develop a new employer brand.
In the past, the AA had been affected by inaccurate perceptions of who they’d be as an employer. With 15 million members and more than 7,000 colleagues, they’re the UK’s largest motoring and breakdown cover organization. However, being known for doing one thing very well was proving to be a barrier to candidate attraction. People thought the only jobs they had to offer were their famous roadside roles. That was far from the truth, but the AA was struggling to attract the talent they needed for their wide range of career opportunities.
Dig Deeper
PeopleScout Webinar: Using Data to Optimize Your Recruiting Process and Employer Brand
The AA needed to challenge misconceptions and engage a much broader audience. And, with a bold new employer brand message at the heart of an ongoing series of innovative attraction campaigns, this is how the AA and PeopleScout did just that – with award-winning, record-breaking results.
Ready for Change
Back in 2016, the AA’s talent acquisition team faced a number of challenges.
Before the arrival of Craig Morgans as their Director of Talent Acquisition, Emerging Talent & Employee Experience, they had no senior talent expert at an influential level. There was no robust workforce planning, a lack of innovation in
candidate generation, and an inconsistent approach to selection.
On top of that they had no discernible employer brand. And, at nearly four years’ old, their careers site suffered from a clunky candidate journey and outdated visuals, compounding their problems with engaging the right talent.
A change in thinking was needed. The AA had to find more imaginative ways to reach and engage with target audiences. At the heart of it all was a plan to develop the employer brand with a strong, authentic central message that would underpin all attraction and engagement activity.
The AA partnered with PeopleScout to develop their dynamic employer brand message. One that would challenge perceptions, do justice to their innovation as a business, and bring the AA culture and diversity of opportunity to life.
Getting The Message Right
We undertook in-depth research to analyze the AA’s culture, offering and opportunities, to articulate the “give” and “get.” Carrying out extensive employee interviews enabled us to understand the key differentiators of all roles in the contact center, road operations and corporate job families. We also looked outside the company, to get a fuller idea of competitors’ market positions and understand what the public thought about the AA.
We developed the emerging themes into pillars that we could validate with real stories from the business, and that could support an engaging creative approach. We refined our thinking to a proposition that really encapsulated the spirit of the
AA. Leading everything was a message that we’d heard over and over.
Working for the AA, people thrived on going the extra mile to help customers with unexpected challenges – and across a surprising variety of opportunities.
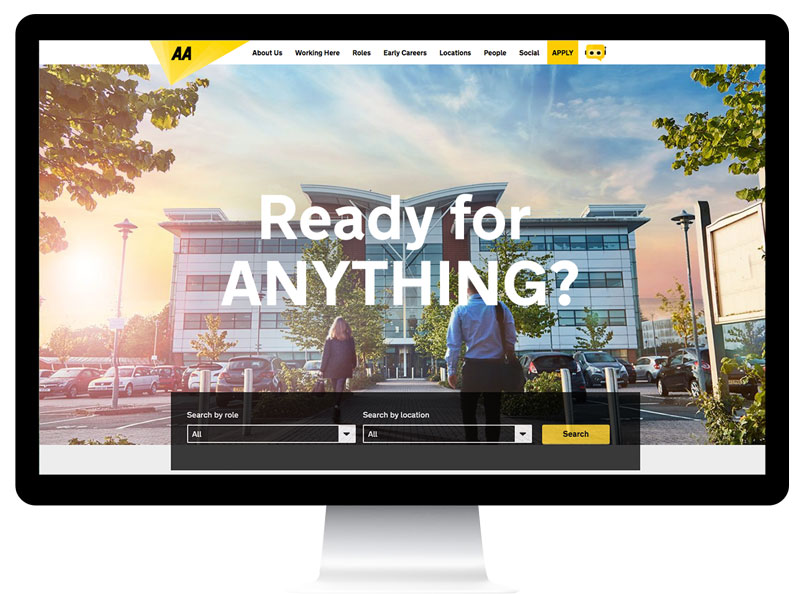
This insight became the AA’s employer brand core message, Ready for ANYTHING? It also acted as the perfect counterpoint to their corporate brand message to customers and members, Because anything can happen.
Putting Our New Platform Into Practice
As the gateway for people to understand the opportunities that might be right for them within the AA, the careers site was the obvious starting point for rolling out the new employer brand. And by launching with this digital shop window, not only could we get the brand experience right, we could also give the site a much-needed technical and UX overhaul.
The new site was launched in February 2017. Creating an engaging, interactive and easily navigable user experience, it’s built around rich content, inclusive photography and video interviews – enhanced with numerous responsive, interactive elements.
The site has evolved, with new elements added over time. As well as showcasing the Almost every role you can imagine employer brand video, the site engages and informs visitors with stories of current employees and realistic job profiles. All of which combine to bring the story of being Ready for ANYTHING? and working with the AA to life. Meanwhile the AA social hub also brings the worlds of social media and blogs into the site, providing an at-a-glance, continuously updated feed of all things AA.
More recently, we’ve added new features, to give site visitors an even more immersive experience – including an insightful 360° tour and assessment tool, plus some interactive 3D imagery to add depth to the visual impression. theaacareers.co.uk is a site designed to surprise, inspire and educate.
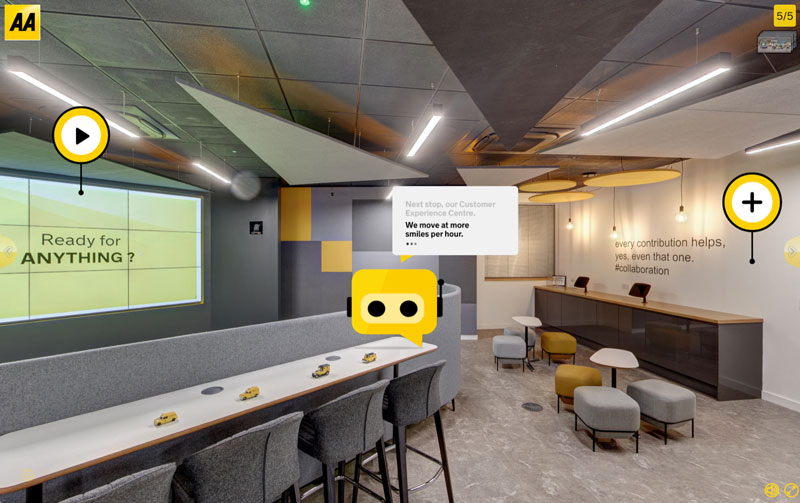

The Chatbot That Shows the Human Side of the AA
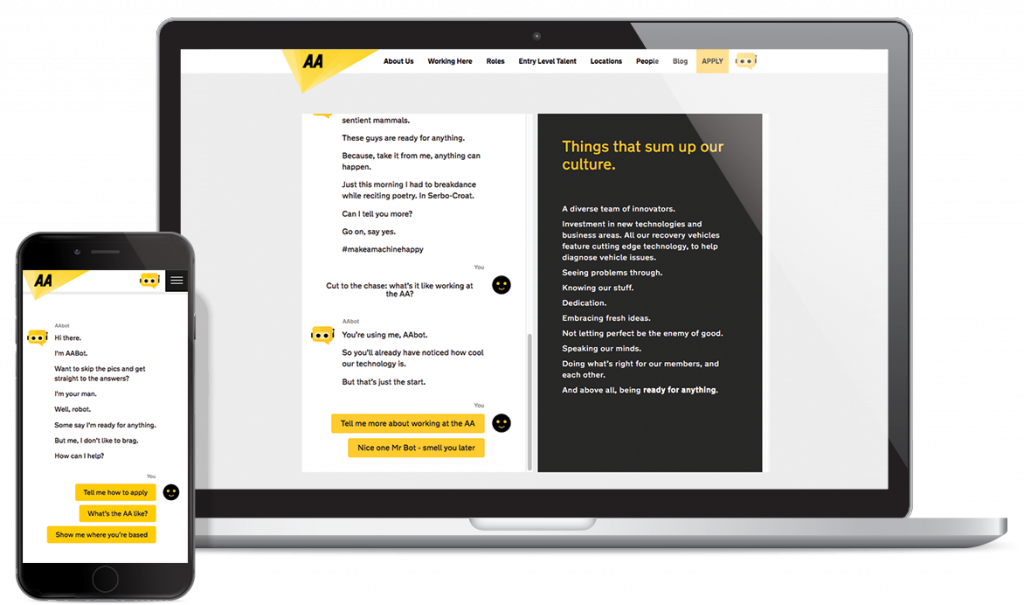
The Ready for ANYTHING? tone of voice was woven into the site and became the voice of the first-ever appearance of the innovative AAbot – a cheeky, wisecracking chatbot that guides users on life at the AA. Demonstrating technological innovation as one of the first of its kind, AAbot was an efficient way to serve visitors the content they were after – and equally importantly, he represented the playful side of the business, showcasing the fun culture that people hadn’t associated with the AA before.
For visitors to the site, this was an unexpected and charming way of bringing the employer brand to life, and together with the improved candidate journey and overall experience, was a rousing success. Site traffic increased 320% and applications increased 266% over an 18-month period. Visitors are engaging with the site for longer too, with page views up 12%, bounce rates dropping 8% and a 10% increase in pages viewed per session.
Tapping the Energy of the Internal Audience
As important as it is to engage an external audience, an employer brand has to reconnect and be embraced internally to mobilize the existing employees as active advocates. AAbot’s charm was used internally, featured on the walls and windows of AA offices and reinforcing the expect the unexpected messaging of the EVP. ReadyforANYTHING? also became increasingly popular with employees who were supported to play an active role in bringing in great new colleagues.


Did You Say Canine Consultants
This new sense of playfulness and surprise would then underpin our next step towards changing perceptions. Having effectively used honest video of employees to convey job opportunities, we wanted to now use video to grab attention of passive audiences, entertain and educate them.
We developed a script that highlighted the diversity of roles the AA offers, creating pretend roles such as Canine Consultants, Rapid Response Pizza Officers and Outer Ozone Patrollers to interrupt the long list of real AA roles. We shot the entire video in a single, continuous take within an AA office, and made sure to feature real employees. AA colleagues were enthusiastic advocates of the content, with more than half of the entire AA workforce watching the video and sharing it widely. The result? The video increased careers site visits by 16%
Getting Out Into the Community
With the success of the video, we became bolder. We’d learned that pushing boundaries helped us succeed in changing the perceptions of passive audiences. So, we decided to take our message to the streets.
We suggested an experiential event for a number of reasons. We wanted a way of raising general community awareness of the AA easily, effectively and creatively. Using a broad brush public approach, we knew that that anyone we engaged might also know others who’d be suitable and interested. We wanted to create an event to take the AA’s employer brand message and see just who was Ready for ANYTHING?. Whatever we did would have to be a great fit with the AA’s fun and friendly culture.
In September 2018, we ran two live events in Birmingham and Newcastle, UK city centers, areas where the AA has a big presence as an employer and lots of roles to fill. We grabbed attention of passers-by in the proud tradition of game shows, inviting audience volunteers on stage to take on a series of increasingly messy mystery challenges. Wasabi toothpaste, a barefoot Lego walk and gallons of slime came together with a celebrity host
in a pop-up competition to bring the spirit of Ready for ANYTHING? to life.
There were lots of laughs, big prizes – and our strategy paid off. The communities local to our contact centers were made aware of the AA as an employer with a really fun culture, visits to the careers site surged, and month-over-month application numbers increased significantly. After the Newcastle event, applications rose from 576 to 1026, with 12 hires. In Birmingham, applications rose from 898 to 1341, with 13 hires. And this was all starting with completely passive audiences.

The Social Side of Talent Engagement
Before working with PeopleScout, the AA had no employment-specific social channels although research shows that candidates expect to be able to shop prospective employers on social. So, we launched separate social media channels for recruitment, recognizing that both the audiences and messaging would be very different from the AA corporate and customer-oriented channels currently in place.
Based on the channel demographics and content structure, we initially selected Twitter and Instagram, and spent the early part of 2018 scoping out a launch program with content pillars, content calendar, internal sponsors, and training for the PeopleScout social media team to give them full responsibility for managing and curating content.
The key advantage of having a team devoted to the AA careers social channels is being able to capture the immediacy that’s vital with any recruitment content – and with built-in knowledge of the AA’s employer brand and talent agend.
Social media has also played a key role in the promotion and delivery of our most recent projects: the augmented reality app-based #wheresbotbeen campaign and competition, as well as Ant Middleton’s 24-hour, live interactive challenge – our biggest, boldest campaign to date.
24 Hours to Prove You’re Ready for Anything
The Ant Middleton 24-hour, live interactive challenge was easily the most ambitious project of our partnership. Aligning with the AA’s long-lasting connection to the armed services, as well as embodying the Ready for ANYTHING? brand,
this campaign was boosted by a relevant celebrity influencer and engaged the general public through live streaming and social media voting.
Six brave employees were chosen to take part in this 24-hour challenge, living and breathing the Ready for ANYTHING?spirit – following the former Special Boat Service soldier through a series of grueling challenges in the Lake District wilderness.
The final lucky half-dozen were chosen from hundreds who responded to an internal communications campaign and applied to take part, in what was highest engagement level ever for a story on The Hub (the AA’s intranet).
We wanted the public and AA colleagues to really root for our chosen contenders during the event, so to get the interest level rising, we filmed their life stories, ready for sharing on social media. They spoke eloquently and compellingly on camera about their lives. We got first-hand stories of drama, heartbreak, courage and transformation.

These videos were posted across Instagram, Facebook and Twitter, and they clearly made a connection with people. At the start of the event, colleagues and strangers alike were rooting for particular contenders.
The event began at 4 p.m. on July 25, 2019. The next 24 hours were packed with unpredictable drama. Events were live-streamed, the pace was relentless, and the AA people got into it just as much as the watching public – commenting, voting, watching and sharing across social media.
We decided to involve the audience throughout. In an unusual twist, viewers could select tasks for the contestants while watching the live stream on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram or on the dedicated site we built for the campaign, Ant24Live.com. Selections varied by type and toughness of tasks such as rafting versus quad biking, or a swim
at dawn versus a planking marathon – keeping audiences engaged throughout the 24 hours (although we did allow the participants to sleep!).
The whole show was streamed to AA contact centers, garages and the corporate office, and thousands of AA employees tuned in, acting as social media cheerleaders and social media amplifiers.

Venturing Into Another Dimension
Using 3D animation and augmented reality (AR) technology, our next project took Ready for ANYTHING? into new territory, with a fun-packed, bespoke-built AR app launched at experiential events.
Keen to embrace new technology to develop innovative ways of boosting brand engagement, the AA asked us to create a fun, unexpected and interactive experience that would help them reach a new audience.
So, we looked at the increasing use of AR to change the way audiences connect with brands. And, we considered how we could use it to engage a passive audience – mainly families, as flexible working patterns at AA contact centers can work around their lives – and increase the AA’s potential talent pool.
When it came to what we’d build our AR experience around, there was a clear direction to take – the AA chatbot, aka AABot, seemed like the perfect character to take us to the next level. Until now, AABot had existed only as a 2D cartoon head. So, we gave him a 3D animated body and made him the star of his own AR app – AABot Drop – compatible with both iOS and Android devices.
We created a fun, interactive installation featuring the AR trigger images, in the form of postcards from AABot, at the Manchester Trafford Center and Birmingham Bullring shopping centers – close to the AA’s Cheadle and Oldbury contact centers.
Using the AABot Drop app, people could see AABot’s animated postcards come to life – either on their own phones, or the iPads we supplied. AABot lives up to the spirit of the AA’s EVP, Ready for ANYTHING? in six animated AR adventures, from
space and deep-sea exploration to crowd-surfing his own rock gig. Animations end on a careers message, driving to theaacareers.co.uk.
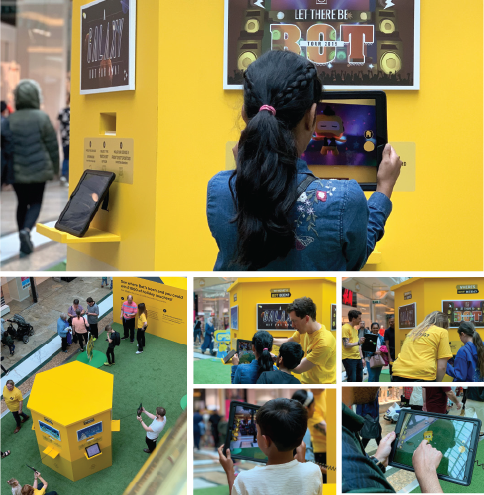

Downloading AABot Drop also gives users interactive, animated images of Bot to play with and position in fun and unexpected places. Sharing their images using #wheresbotbeen, people could enter a competition to win holiday vouchers. Promoting the app and competition across social media got more people involved – and amplified our message. Bot’s postcard trigger images and #wheresbotbeen photo gallery are now housed on the AA careers site –along with app download links – supporting longer term engagement beyond the initial competition.
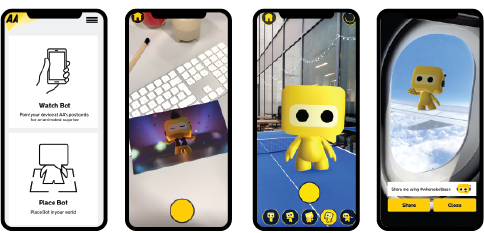
Both events saw good interaction with both young people and families – two key AA contact center demographics. The Manchester event boosted careers site visits by 869%, with applications up 40% week-over-week. After the Birmingham event, careers site visits increased by 535%, with applications up 820% week-over-week.

With hundreds of app downloads and ready for more, we plan to run further AABot Drop-based campaigns with updated AABot scenarios. So, much more than a one-off AR adventure, this can help promote the AA’s employer brand and opportunities to an even wider audience during a longer period of time.
Taking the EVP 2,620 Miles Further
The AA also sponsored adventurer and influencer Anna McNuff’s Barefoot Britain challenge. As someone who champions the idea of being Ready for ANYTHING?, Anna undertook the mammoth task of running the equivalent of 100 marathons barefoot through all kinds of terrain, weather and unexpected challenges to inspire young women. She wants to encourage them to have the confidence to step out of their comfort zone – to see just how much they can achieve when they reach for what seems impossible.
A series of short videos sharing her adventures, along with Anna’s own social posts and support from PeopleScout, have helped to raise brand awareness and promote AA careers to more female talent.
Groundbreaking Activity Leads to Record-Breaking Results
Since the launch of Ready for ANYTHING?, the AA’s internal employee and social media engagement, site visits and application numbers have soared across all brand-led activity. This strong employer brand, combined with a desire to innovate and brave campaign execution, has enabled the AA to move from 60% agency use to less than 5% in 30 months, saving nearly $9 million per year. Meanwhile, the AA’s Ready for ANYTHING? attitude helped it to win 17 recruitment industry awards in two years, including Best Employer Brand at the Recruitment Marketing Awards 2019. And, of course, the AA is always ready to do more.
“This is transforming how we engage candidates, and it wouldn’t have been possible without a true partnership. PeopleScout has risen to our challenges with some genius, wacky thinking!”
– Craig Morgans, Director of Talent Acquisition, Emerging Talent & Employee Experience