Uncertain Times & An Uneven Economic
Landscape
The closing
months of 2019 also brought to a close a decade of strong economic growth and
robust labor markets for many of the world’s leading economies. However, the
disruption caused by trade disputes and uncertainties have produced the first
signals that this long period of sustained expansion may be coming to an end.
Among the unresolved issues that continue to affect the global economy are:
- The
U.S.-Mexico-Canada trade agreement, which was negotiated to replace NAFTA, has
yet to be ratified by the legislature of all three nations. Author’s note: There may be a vote in the
U.S. Congress in the coming weeks after a deal was struck by the Democratic
leadership and the White House.
- The
ongoing trade war between the U.S. and China, the world’s two largest economies,
continues and may continue into 2020.
- Uncertainty
over Brexit continued until the UK election on December 11, which very likely
cleared the way for its departure from the European Union. Even with a firm
Brexit date, a final trade agreement with the European Union has yet to be
completed, and negotiations will be closely watched.
While job growth continued unabated in the labor markets of many key economies, the growth came at a slower pace than in 2018. Some of the most developed economies saw the period of sustained job growth halted and some unemployment rates began to climb. In addition to trade uncertainty, political upheaval and natural disasters also had negative effects on important economies in far-flung parts of the world.
Slowing Job Gains & Job Losses Materialize in the Labor Market
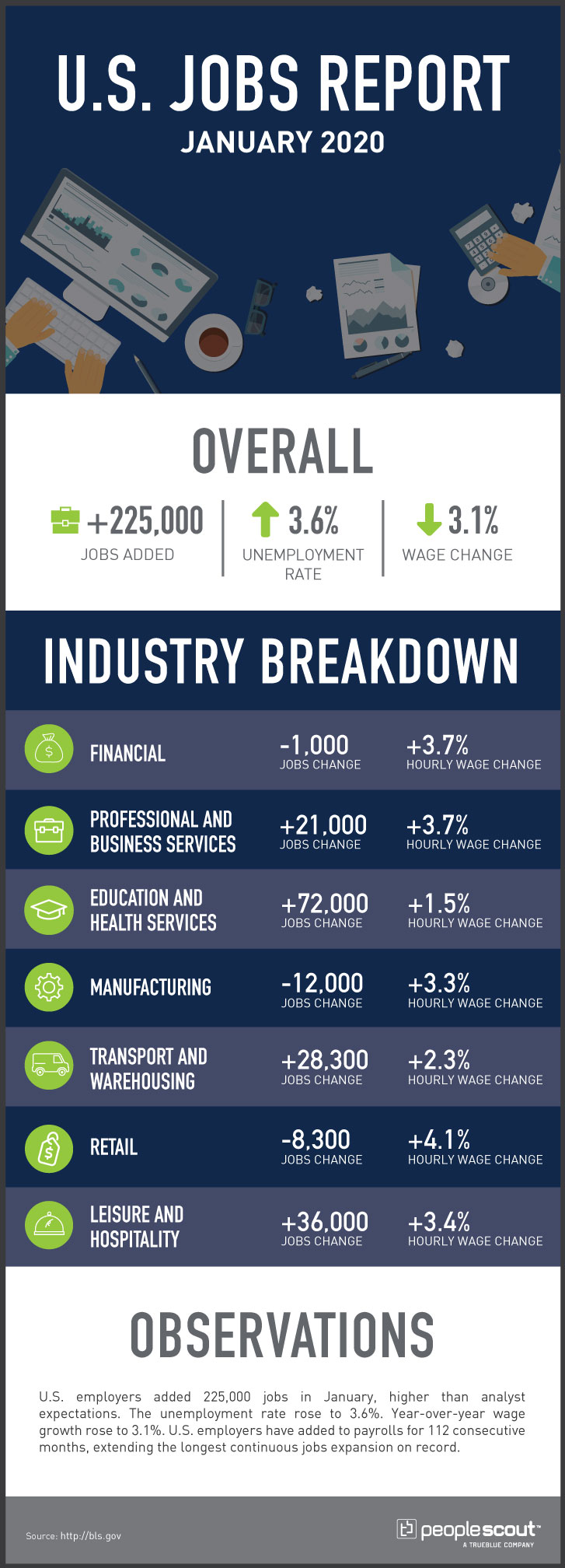
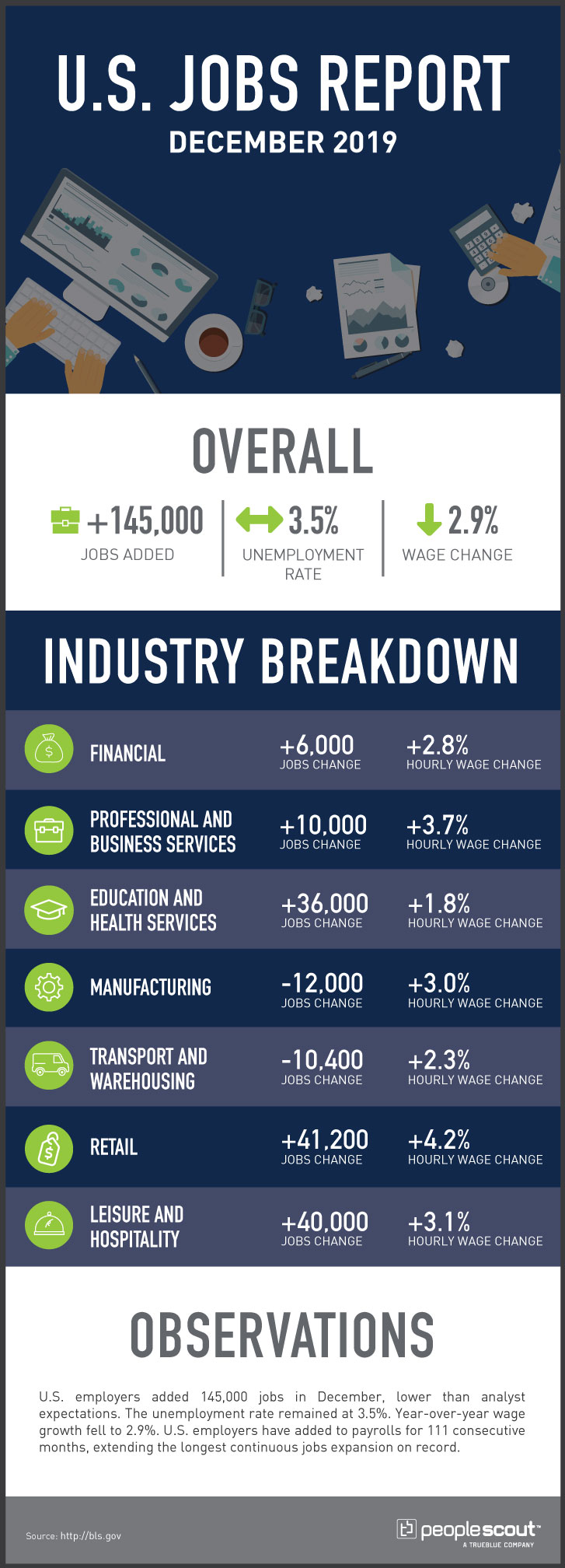
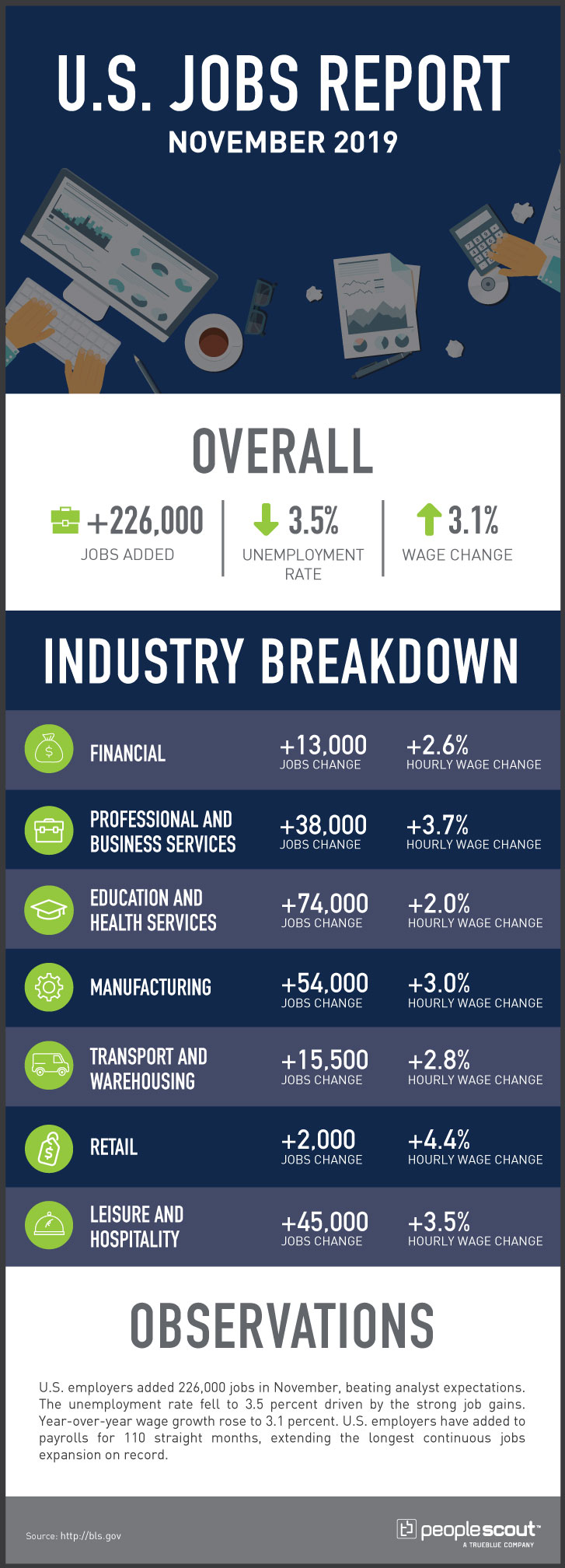
The U.S. labor market added 266,000 jobs in November and posted an unemployment rate of 3.5%. November’s results capped 110 months of continuous job growth, the longest period of sustained expansion in the nation’s history. The year began with an unemployment rate of 4% in January, which was the highest level all year. After hitting a half-century low of 3.5% in September, the unemployment rate rose slightly in October, only to come down to tie the fifty-year record level of 3.5%. While job openings steadily decreased to approximately 7 million, this level of openings was still larger than the number of unemployed Americans.
Additionally, the average monthly job growth improved to 180,000 per month in the 12 months leading up to November 2019. However, at the same time last year, the monthly average of jobs created was 223,000. So, while the job market was expanding, it did so at a slower pace than it did in 2018. The sectors that lost some jobs or grew at an anemic rate include manufacturing and retail. And, while manufacturing was disrupted by strikes and ongoing trade disputes, the diminishing jobs in retail were largely caused by the growth in online shopping, which has brought about a so-called “retail apocalypse” in the U.S. and elsewhere.
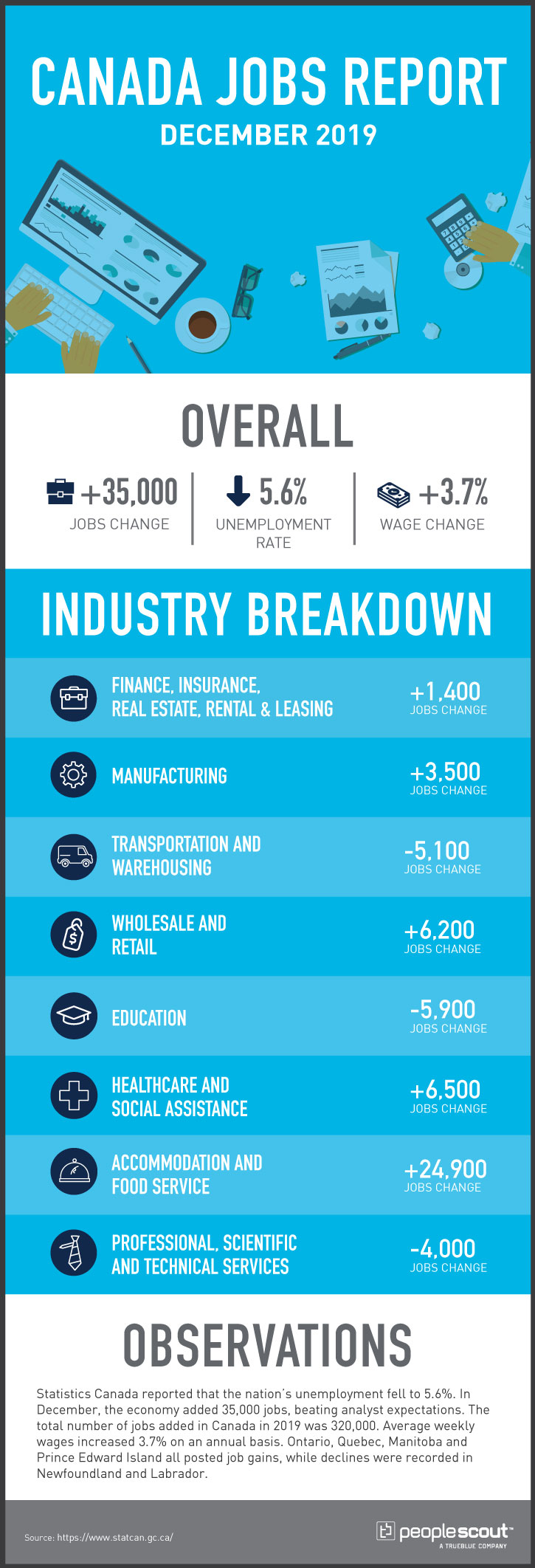
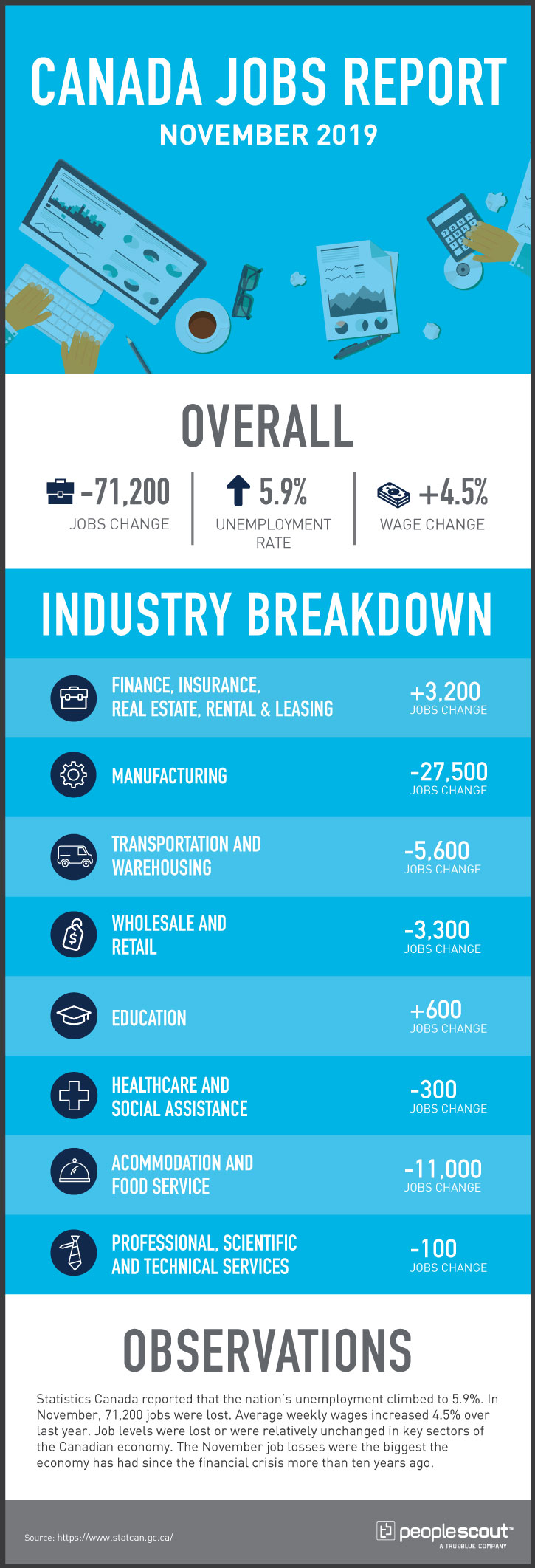
Canada’s employment numbers were positive in much of the first half of the year and grew worse as the year wore on. After losing less than 2,000 positions in October, Canada’s economy shed 71,200 openings in a single month in November. While more than half of those (45,000) were lost in Quebec, other provinces also lost jobs and none had any notable job gains. Canada’s unemployment jumped 0.4% in November alone, reaching 5.9%. From a national perspective, the weak job outlook was not confined to manufacturing and retail as it was in the U.S.; although these were certainly weak in Canada, as well, it also extended to most major sectors of Canada’s economy.
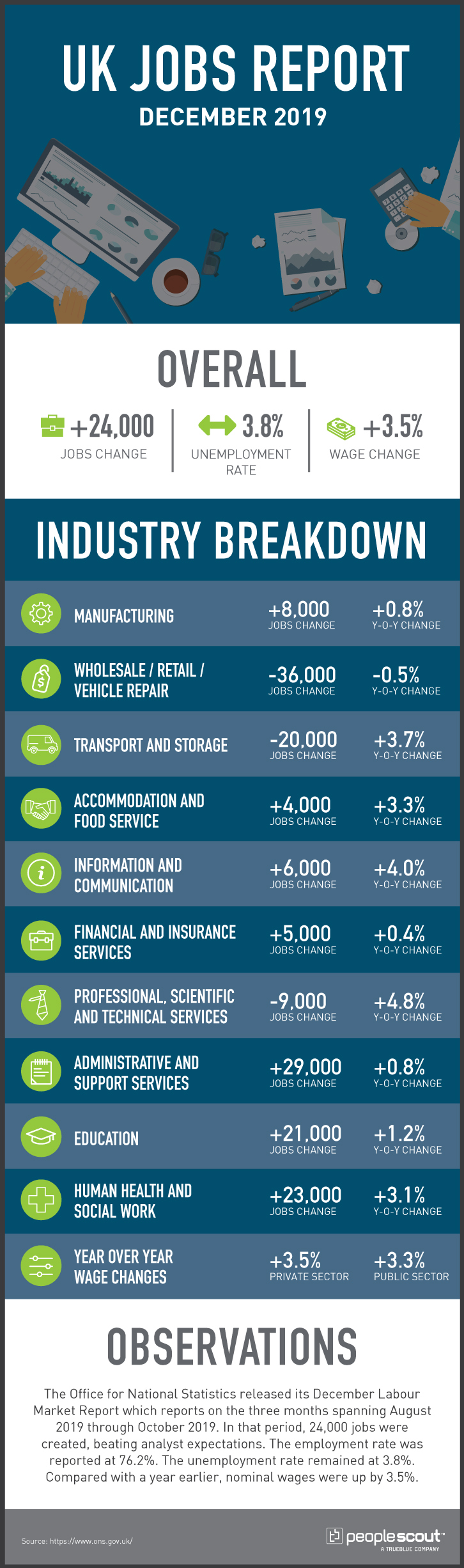
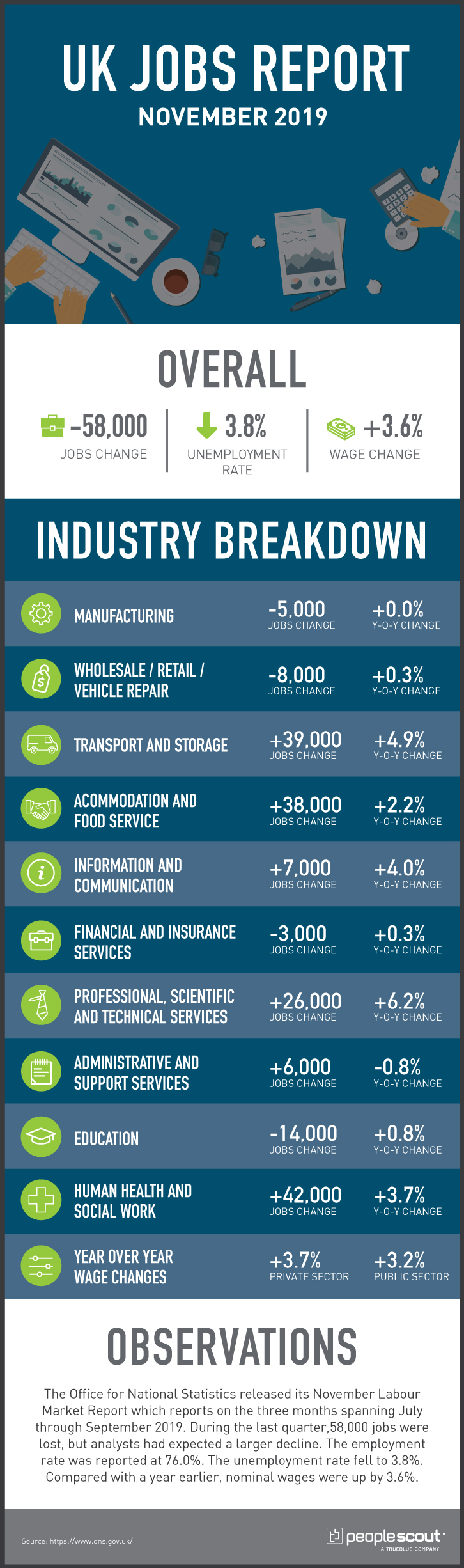
In Europe, the economic landscape was mixed, with most major labor markets posting low unemployment rates that varied little from earlier in the year. In the UK, 58,000 jobs were lost in the quarter ending in September 2019. This was the second consecutive report with posted job losses, many of which analysts blamed on the uncertainty surrounding Brexit. However, the quarter ending in October showed a modest job increase of 24,000 positions, pushing employment to its highest level ever. Yet, even in the months when employment fell, the unemployment rate also dropped to a low 3.8%, which held steady in the August-October quarter; the UK unemployment rate has not been lower since 1974, well before the living memory of much of the UK workforce. And, while the results of the December national election opened the path for a departure from the European Union in early 2020, provisions of an eventual trade agreement between the UK and the EU remain to be seen.
Elsewhere in
Europe, the Eurozone’s unemployment rate was 7.5% in October, the same as it
was in June, but 0.3% lower than it was at the end of the first quarter. France
posted an unemployment rate of 8.5%, falling from 8.7% in June, while Germany’s
low unemployment rate of 3.1% in October was unchanged from its level in June.
In the Asia-Pacific region, unemployment rates rose in some leading labor markets, but only to relatively low levels. During the third quarter, China’s labor market reported an unemployment rate of 3.6%, a full percentage point higher than in the second quarter. Japan’s rate rose just 0.1% from June to October, landing at 2.4%. After experiencing considerable unrest, Hong Kong’s unemployment rate rose to 3.1% in October – from just 2.8% in June. And, in contrast with the rise in unemployment in other Asian powerhouses, South Korea’s unemployment rate fell an entire percentage point from June to October, ending at 3%. India’s labor market also had a drop in unemployment, falling 0.4% since June, to 7.5%.
The Oceania economies also posted mixed unemployment numbers from their respective labor markets. Australian unemployment was just 4.9% in February, an eight-year low, but it has been higher ever since, rising to 5.3% in October. New Zealand reported that its unemployment rate had fallen to 3.9% in the second quarter of this year – down from 4.3% at the end of 2018 – but then rose to 4.2% in the third quarter.
Wage Increases Outpace Inflation in Key Labor Markets
Annual wages have continued to grow faster than the rate of inflation in most leading economies. The U.S. annual wage increases stood at 3.1% in November, coupled with an inflation rate of less than 2% in the third quarter. In the UK labor market, nominal annual wages rose 3.5% in the quarter spanning August through October, which was also comfortably ahead of inflation. During the same period last year, nominal wages increased 3.3% annually, and the unemployment rate was 0.3% higher. Both the U.S. and UK posted higher annual wage gains earlier in the year, but the increases were not substantial relative to the tight labor markets in each country during much of the year. There is no clear consensus among economists as to why wages have not risen faster during the current sustained period of low unemployment.
In the Canadian labor market, annual wage gains fluctuated sharply during 2019; in May, they were just 2.1%, rising in July to 4.6%, but falling to 3.8% in September before landing back at 4.5% in November. This rising rate of wage increases came during the same month that Canada experienced its greatest job loss since the financial crisis.
Australia
instituted the highest minimum wage law in the world on July
1, 2019, but annual wage growth continued to be sluggish; year-over-year wage
growth fell to just 2.2% in November, and Australian wage increases have been
stagnant for some time. The last time the annual rate of increase was just 1%
higher was in late 2012. And, without the robust minimum wage introduced earlier
this year, wages could have potentially grown even more slowly. With
unemployment above 5% for most of the year, analysts are not predicting
significant wage gains until the labor market improves.
Political Unrest & Devastating Fires
Massive street
demonstrations erupted in Hong Kong and in capitals around Latin America during
the closing months of 2019, leading to significant economic costs. The capitals
of Bolivia, Chile and Ecuador were roiled by anti-government protests. Specifically,
Chile – which is considered by many to be an economic success story – had a
3.4% annual retraction in its economy in October, which was triggered by its civil unrest. As a result, the
government agreed to a referendum to replace the constitution, and announced
plans for a $5.5 billion economic stimulus package.
Similarly, protests in Hong Kong intensified after months of ongoing demonstrations and led to a shutdown of the city’s airport; traffic was also disrupted and major thoroughfares turned into sites of violent confrontations. The effects of the protests on Hong Kong’s economy have been devastating. In the retail sector alone, 7,000 firms are expected to close, and many of those that survive plan to lay off employees. Moreover, the government is forecasting a contraction of 1.3% for Hong Kong’s economy in 2019 – the first annual decline since the Great Recession in 2009.
Furthermore, powerful wildfires broke out in both California and Australia, causing extensive destruction and exacting economic costs in their respective economies. Workers in Sydney and other areas close to the fires struggled with smoke-filled air and, consequently, concerns for their personal health and safety. Meanwhile, in California, fires changed the landscapes of entire communities, and power was regularly cut off as a preventive measure to keep the fires from spreading.
The relentless threat of new wildfires and the intensity of the destruction of this year’s infernos have led some to conclude that the seemingly endless potential for prosperity in the nation’s largest state is over, and that this is the end of California as we know it. The fires in both places led to dislocations and business interruptions. While political unrest will inevitably fluctuate and appear in different locations around the world, destructive fires in both the western U.S. and Australia have become the new normal, and will likely continue to be a factor in the affected regions in the years to come.