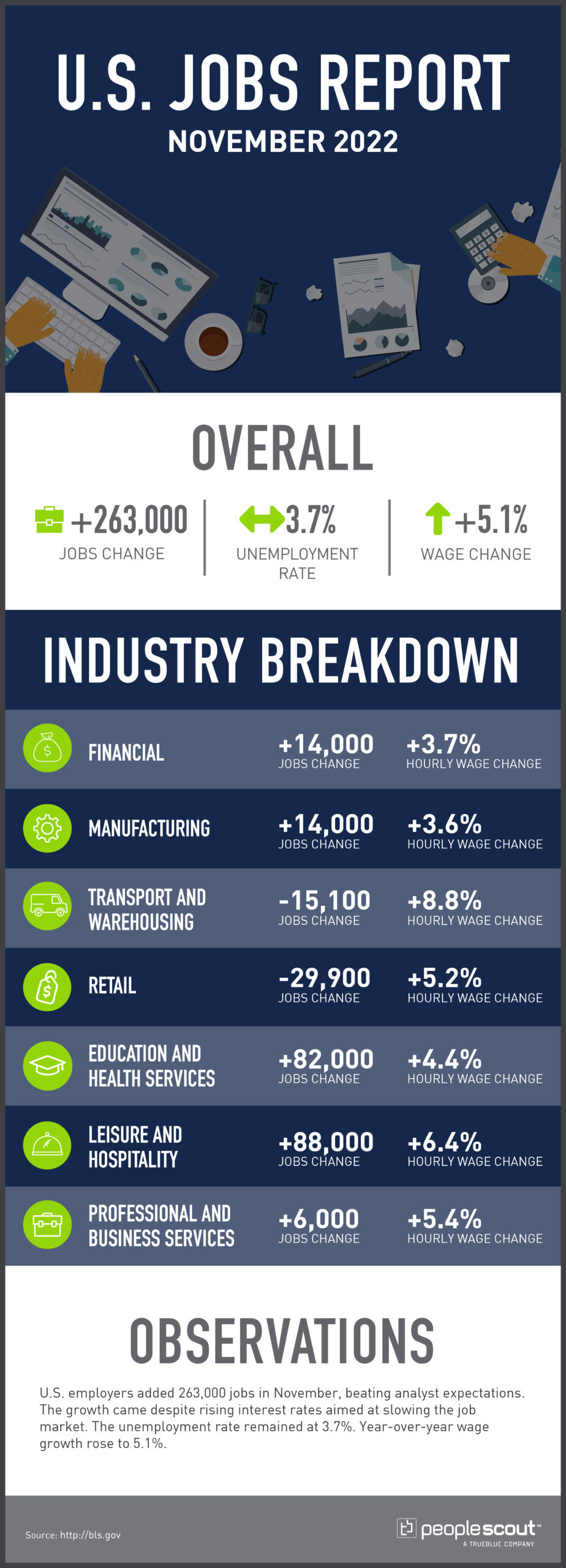
U.S. employers added 263,000 jobs in November, beating analyst expectations. The growth came despite rising interest rates aimed at slowing the job market. The unemployment rate remained at 3.7%. Year-over-year wage growth rose to 5.1%.
The Numbers
263,000: U.S. employers added 263,000 jobs in November.
3.7%: The unemployment rate remained at 3.7%.
5.1%: Wages grew 5.1% over the past year
The Good
While the overall jobs number remained higher than expected in November, the growth was not spread evenly across industries. Service-based industries like leisure and hospitality and education grew, while goods-based industries like retail and transportation and warehousing saw jobs losses. As the New York Times reports, these numbers show that while employers are being more cautious, they are still finding reason to expand.
While the U.S. job market has fully recovered the number of jobs lost at the start of COVID-19 pandemic, some industries lag behind their 2019 jobs numbers, like leisure and hospitality. Those industries largely drove November’s growth.
The Bad
As MarketWatch reports, November’s jobs data is not promising when it comes to reducing inflation. Year-over-year wage growth jumped back up to 5.1%—significantly higher than the Federal Reserve’s goal. November alone saw a 0.6% jump in wages, which is more than double what is expected.
The Unknown
The Federal Reserve is set to meet in two weeks, and as the Wall Street Journal reports, November’s jobs numbers make it likely that officials will raise interest rates about 0.5%. This comes after four straight .075% increases. Fed Chair Jerome Powell has said that some prices that rose significantly in the past year, like used cars and housing could fall in 2023 but that “despite some promising developments, we have a long way to go” when it comes to inflation. To decrease inflation, experts will watch carefully in the next year to see how high and for how long the Federal Reserve will raise rates.



