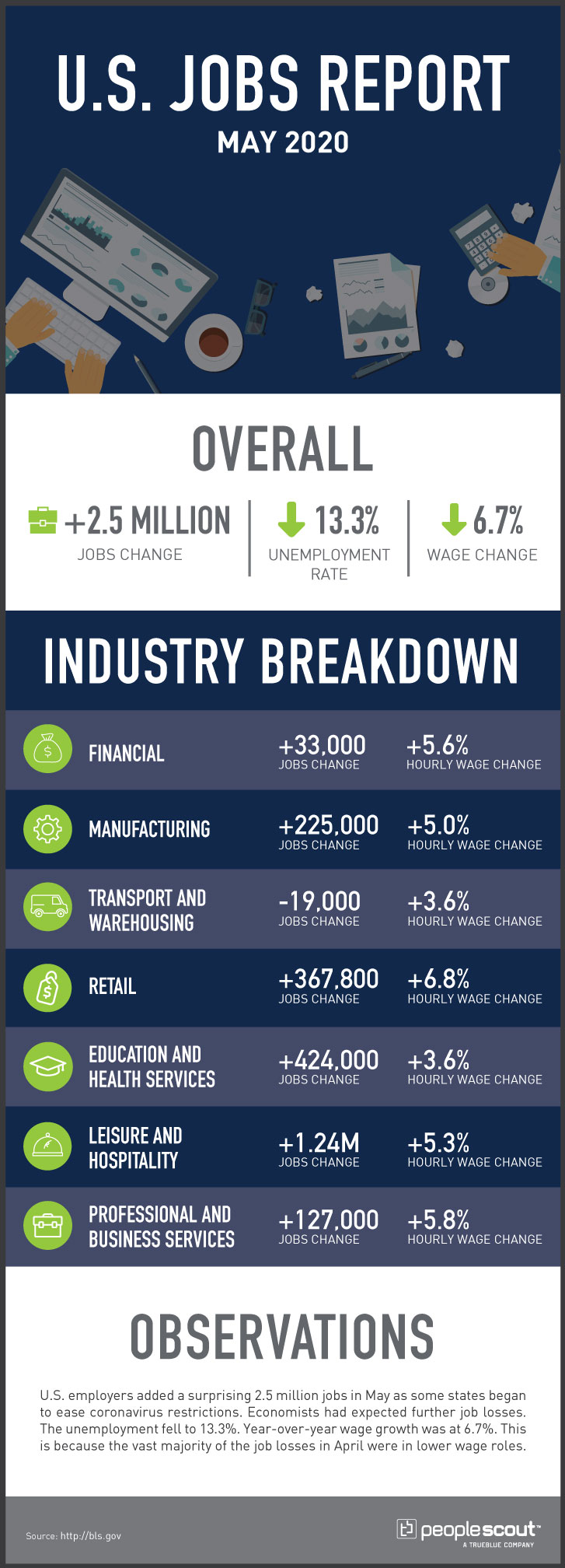
In a surprising May jobs report, the Labor Department reports U.S. employers added 2.5 million jobs as some states began to ease coronavirus restrictions. Economists had expected further job losses. The unemployment rate fell to 13.3%. Year-over-year wage growth was at 6.7%. This is because the vast majority of the job losses in April were in lower-wage roles.
The Numbers
2.5 million: Employers added 2.5 million jobs in May.
13.3%: The unemployment rate fell to 13.3%.
6.7%: Wages increased 6.7% over the last year.
The Good
The May numbers surprised economists and point to good news. According to MarketWatch, analysts had expected the May report to reflect a third straight month of job losses—a predicted loss of 7.25 million. Economists surveyed by Dow Jones expected an even worse 8.33 million loss. However, in May, employers added 2.5 million jobs, the highest single month gain since records began in 1948.
Nearly half of the job gains came in leisure and hospitality, a reflection of restaurants reopening as some states began to ease coronavirus restrictions. Additionally, many bars and restaurants received assistance from the government Paycheck Protection Program. This indicates that the U.S. economy may be on the road to a faster than expected recovery from the coronavirus pandemic.
According to CNBC, the job gains nearly perfectly mirror the 2.7 million Americans who had reported their layoffs as “temporary.” Economists had been concerned that many of those layoffs would become permanent.
The Bad
While the large increase in employment is good news, the unemployment rate is still higher than any other recession since the Great Depression. Additionally, a broader measure of unemployment that includes jobless workers, those working part time and those who have given up the job search because they are too discouraged was at 21.2%, according to the Wall Street Journal.
The unemployment rate also varies based on gender and race. The rate for Hispanic and Latino workers was 17.6% and it was 16.8% for black Americans. While Asian-Americans face 15% unemployment and white workers are at 12.4%. The unemployment rate is also higher for women.
Job postings have also started to rise but are still far below the pre-pandemic numbers.
The Unknown
The COVID-19 pandemic leaves employers and economists with a lot of unknowns. As the New York Times reports, the $2.8 million stimulus is still helping the economy, but much of that assistance is set to end over the summer, including the enhanced unemployment benefits, which are set to end at the end of July.
It is also unclear how long companies can survive with decreased business, as many consumers choose to stay home and spend less. Additionally, experts worry about a second surge in coronavirus cases, which could hit in the fall.



